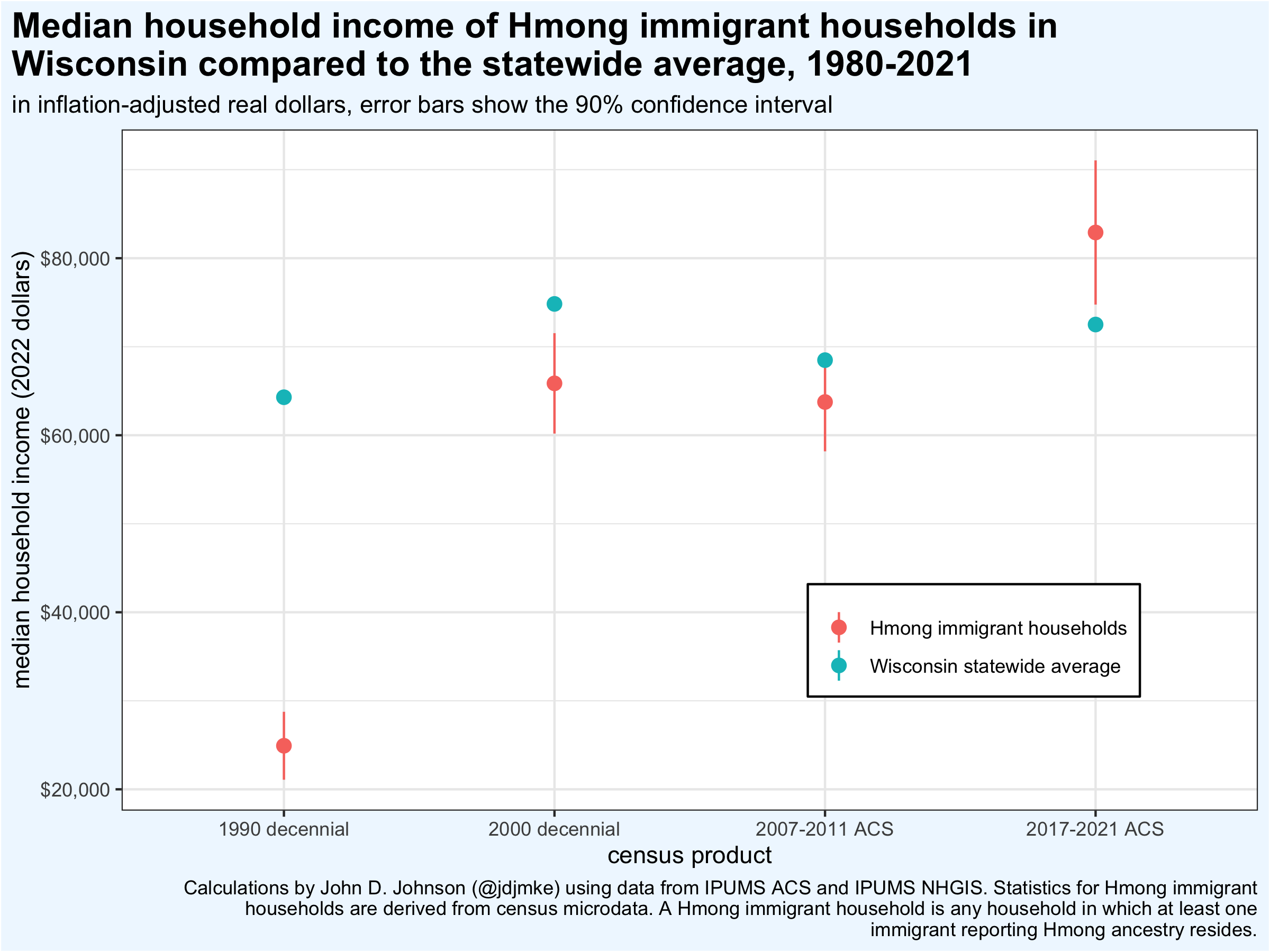
The typical household income for a Hmong immigrant to Wisconsin now slightly exceeds the state average, recent census data shows.[i] This follows a dramatic rise in incomes among Hmong immigrant families over the past three decades.
Most Hmong immigrants arrived in the United States during the 1980s, as part of the refugee resettlement program. Like most refugees, they reached America with little besides themselves. In 1990, the median Hmong immigrant household reported a total income of $25,000 (in 2022, inflation-adjusted dollars). This was over 60% less than the state median of $64,000.
By 2000, the average Hmong immigrant’s household income was 12% of the state median. The gap further narrowed by the end of the decade, with the statewide estimate falling within the margin of error for Hmong families.
In the latest census data, collected between 2017 and 2021, the median household income for Hmong immigrants stands at $83,000, compared to $73,000 statewide. This difference is statistically significant, exceeding the 90% confidence interval for each estimate.
The first large wave of Hmong refugee resettlement in the 1980s was followed by a wave of negative media portrayals. Wausau, Wisconsin, became a national touchpoint. In 1994, the Atlantic Monthly published a widely-read 6-thousand-word article “The Ordeal of Immigration in Wausau.” 60 Minutes ran a segment on the same theme.
Wisconsin reporter Rob Mentzer, revisited the piece in 2014, writing:
“Twenty years later, though, even the Atlantic Monthly piece seems not so much prescient as dated. Its predictions didn’t come true, and it’s shot through with a sense of racial anxiety — southeast Asians are taking over this fine white city — that feels gross.
The author of the piece, Roy Beck, achieved national fame from it, and its publication set him on a career path that would make him arguably the nation’s leading anti-immigration voice, as founder and director of the advocacy group NumbersUSA. In a profile this month, The New York Times called him “perhaps the most powerful member of the small but vocal movement that has helped scuttle every effort at an immigration overhaul for nearly two decades.”
Hmong Wisconsinites have continued to face challenges, as an Atlantic article by Doualy Xaykaothao, “To Be Both Midwestern and Hmong,” described in 2016. But it is simply not the case that Hmong people have failed to thrive in places like Wausau. On the contrary, the average household income of Hmong immigrants has more than tripled over the past 30 years, now exceeding the state average for all residents.
Footnote
[i] The Census Bureau does not publish estimates of household income by reported ancestry. I calculated statistics for Hmong immigrant households using census microdata retrieved from IPUMS USA at the University of Minnesota. I define a Hmong immigrant household as any household in which a foreign-born person reporting Hmong ancestry resides. I adjust each year’s data for inflation using the CPI-U-RS All Items time series.

In the 1980s to early 1990s, there were a similar backlashes in Fresno, California, where 60-70% of the Mong families were on public assistance. The Mong were being labeled as lazy and that they had nothing to do but were there to make babies only. Today, those immigrant parents are now mostly gone. It’s their children and grandchildren who were able to obtain higher education and, thus, are able to climb the economic ladders much more successfully today.